Path in Python#
One important task when dealing with batches of data is accessing and reading files in
folders. In Python, some libraries can be used to handle filesystem paths such as os and glob but here we will focus on pathlib library.
Feel free to use os and glob library if you are already familiar with them.
Benefits of pathlib library#
No more cumbersome use of
osandos.pathfunctions.Contains the semantics of different path types.
Well-defined semantics, eliminating any ambiguities
Useful Methods#
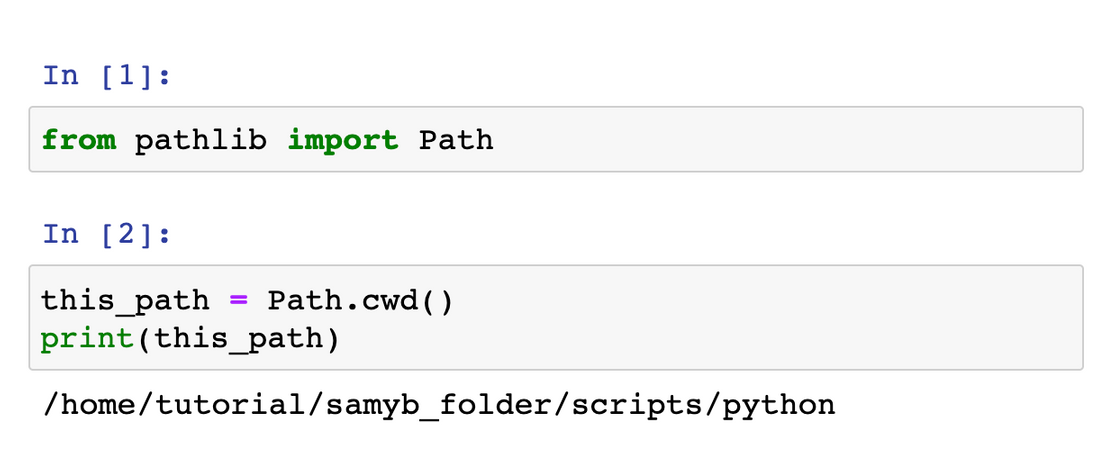
Path.cwd(): Return a new path object representing the current directory.
Example
Let us try to see the folder we are currently in. (Using Jupyter Notebook, you can go to your folder and make a new Jupyter Notebook file.)
Path('/filepath').iterdir(): When the path points to a directory, yield path objects of the directory contents.
Example
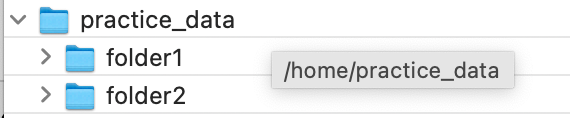
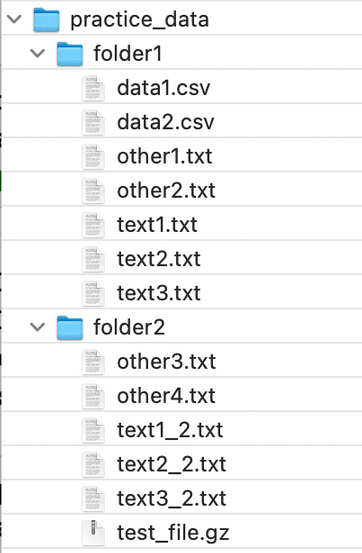
Let us check all the files in this directory: /home/practice_data.

Path('/filepath').exists(): Whether the path points to an existing file or directory.
Example
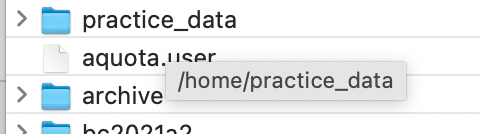
Let us check a folder in /home/ directory called practice_data. This folder cannot be accessed directly from Jupyter Notebook.

Path('/filepath').glob(*pattern*): Glob the given relative pattern in the directory represented by this path, yielding all matching files.
Example
Let us get the path for all the .csv files in thisdirectory: /home/practice_data.

Tip
The “**” pattern means “this directory and all subdirectories, recursively”.
Practice 7#
Make a program called combining_files to combine all the files starting with “text” from folder1 and folder2 in /home/practice_data. Save the combined files as combined_files.csv in your folder.
Steps
Make a new Notebook first. Rename the title to be
combining_files.Use
globwith pattern'**/text*'to get the list of all files starting with the word “text”. Save it in a variablefiles_list.Import
pandasand use a list comprehension to make a list of DataFrames containing all the files infiles_list. For example:df_list = [pd.read_csv(file) for file in files_list].Use
pd.concatto combine all the DataFrames indf_list. Save the result in variabledf.Use
df.to_csv('combined_files.csv',index=False)for writing the result of Step 3 into a .csv format.
Note
Give screenshot of the code and the content of combined_files.csv (you can open it using Jupyter Notebook).
Practice 8#
Save the first and second columns of test_file.gz in folder2 as a DataFrame then save it as yourname_test_split.csv and put it in /home/yourgroupfolder.
Tip
You can experiment with formats other than
.csv. For example,.parquetis a good choice if you have categorical data.
Steps
Make a new notebook.
Save the path for
test_file.gzin a variable calledfile_path.Import
pandasand read the file usingpd.read_csv(file_path, compression='gzip', header=None, sep='\t'). Save it in variabledf.Get the 1st and 2nd columns using
df.iloc. Save it in a variablenew_df.Use
new_df.to_csvto savenew_dfinto a .csv file. (Not in your folder but in your group folder!)