Introduction to job scheduler#
Due to the sheer amount of data we have and the processing required to handle it, one server may not be enough for our needs.
Additionally, if multiple users are using the system at the same time, our program may take much longer than expected.
Computer Cluster#
A group of nodes (computers or servers) that can be used to execute programs. Because each node is its own separate computer, programs can be run on different nodes so they don’t interfere with each other.
Job queue#
A job queue is a list of jobs (programs) that will be run on the cluster. The queue is managed by a job scheduler, which determines the order that the jobs will run.
Job scheduler#
A job scheduler is the interface between users and the cluster. First, users create programs and submit them to the job scheduler. Next, the job scheduler adds the job to the job queue and waits until a node in the cluster has the requested resources available. Finally, the scheduler sends the job to the node and keeps track of the state of the job.
The scheduler also keeps track of which resources are in use and uses this information to assign jobs to different nodes. This prevents any single node from being overloaded.
Our job scheduler: Son of Grid Engine#
Son of Grid Engine (or SGE for short) is an open-source, versatile, and highly scalable distributed resource management application.
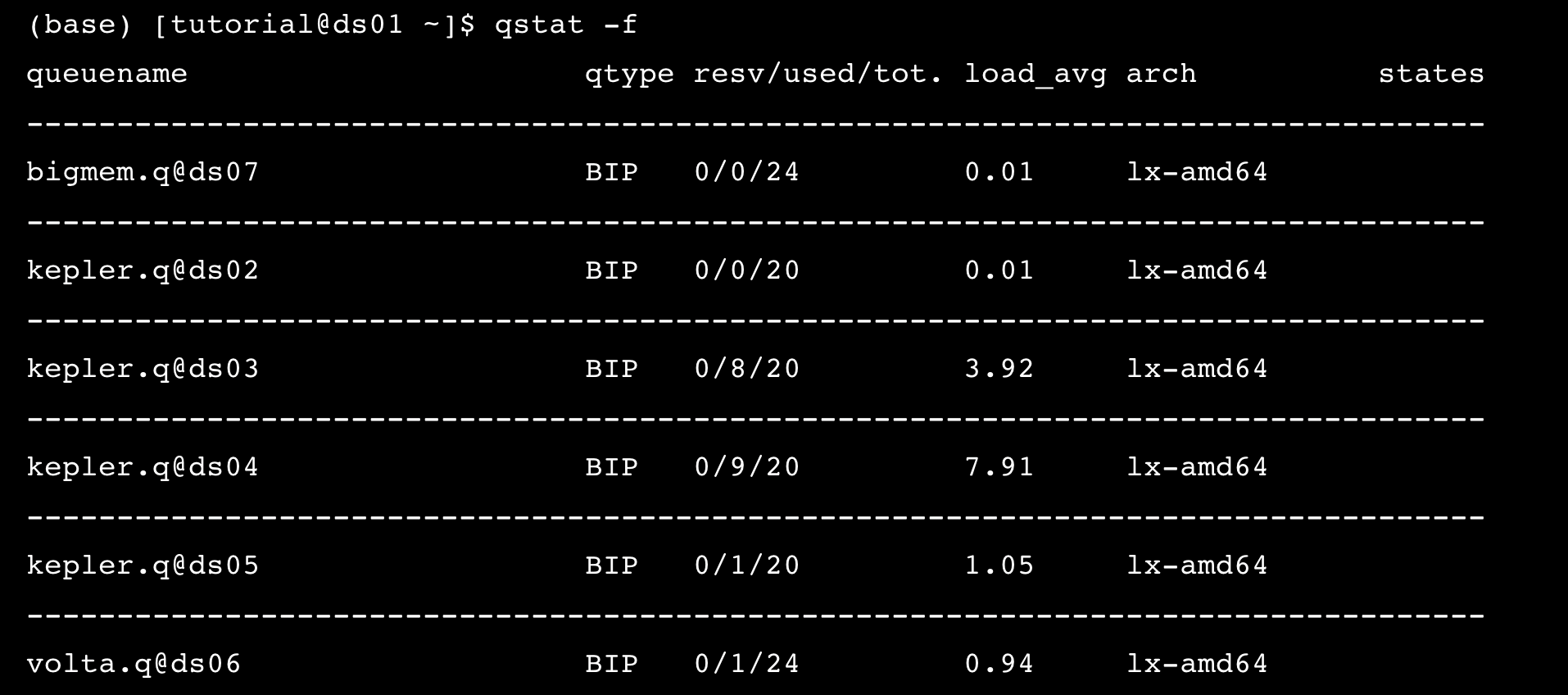
In total, we have 7 compute nodes, and the login node, ds01. To check the availability of all virtual machines, use the qstat -f command.
Expected output
Machine specs
Node |
CPU cores |
RAM |
GPU |
|---|---|---|---|
ds01 |
20 |
128 GB |
- |
ds02-05 |
20 |
128GB |
Kepler x 1 |
ds06 |
24 |
96GB |
Volta x 1 |
ds07 |
24 |
1536GB |
- |
ds08 |
32 |
512GB |
Ampere x 4 |